
The most amount of diffraction happens when the wavelength is a similar size to the gap. At the interface between two media, part of the light is reflected, and the other part passes through the interface with a modified propagation direction: this. Two of the more important are that this property is the basis for the diffraction grating that can be used to separate light into its constituent colors, and that diffractive effects set an absolute limit on the quality of an image observed through an optical instrument such as a telescope. Why do prisms do what they do to light How do sound waves spread And why do refraction and diffraction sound the same, but act so different Answers inside. (a picture would help to explain this)ĭiffraction: Waves spread out as they enter an aperture (gap). Diffraction has a number of consequences for astronomy. Diffraction Which of the above properties are common to all. As it slows down it changes direction, meaning that the angle that it is travelling at changes - the angle becomes closer to the normal. Refraction: When light travels from air into another material (such as glass) at any angle other than normal (perpendicular), it slows down. Light diffraction through glass diagram You can also see that the rule from earlier still applies: when the light enters the glass the ray is bent towards the normal. Refraction is the phenomenon that takes place due to the bending of light when it travels from medium to another. Remember that in reflection the angle of incidence (this is the angle that the initial wave makes from the normal), is the same as the angle of reflection (the angle that the reflected wave makes from the normal). A wavelength and speed change are always present when refraction occurs while diffraction is the bending of waves around obstacles and openings. Physics Optics Refraction Of Light Refraction of Light We know that light is a form of energy and can undergo various phenomena like diffraction, reflection, refraction, interference, and polarisation. Reflection: This is when a wave hits a surface (e.g light hitting a mirror) and is bounced back. On the diagram it is useful to mark on a line for 'normal', this is a straight line that is perpendicular (makes a 90 degree angle) with a surface. Importance of double slit refraction problems.
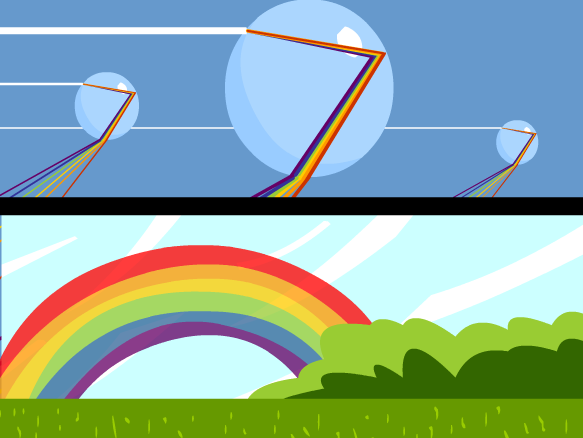
It can also be helpful to draw diagrams of each to help you to remember the difference. Says that light must be a wave because that would explain diffraction. These are all properties of waves and their definitions are useful to remember for exams.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
